Despite a recent dip in its share price, Nvidia’s data center business saw an impressive 409% year-over-year growth in the last quarter, with CEO Jensen Huang forecasting an additional $1 trillion in data center investments over the next four years. Rapidly becoming Nvidia’s most prominent business unit, this growth is fueled by the rise of AI. However, it also brings increased scrutiny on the data center industry to manage the rising demands on power consumption efficiently.
Whether it’s a small server room or a large data center, monitoring equipment, environmental conditions, and power management is crucial to prevent costly downtime and maintain operational efficiency. HMI/SCADA software offers a sophisticated, user-friendly solution for monitoring and managing these critical systems.
Rising energy costs and growing environmental responsibilities have pressured the data center industry to enhance its operational efficiency. As data centers consume vast amounts of electricity to power servers, cooling systems, and other infrastructure, the financial burden of energy consumption has become a significant concern. At the same time, increasing global awareness of climate change and the push for sustainable business practices have placed the spotlight on data centers to reduce their carbon footprint. Regulatory agencies and corporate sustainability goals drive data center operators to find innovative ways to minimize energy usage, optimize cooling methods, and integrate renewable energy sources.
This has led to a surge in demand for energy-efficient technologies, such as advanced monitoring systems, AI-driven workload management, and more efficient hardware solutions designed to reduce power consumption without sacrificing performance. Balancing the need for ever-growing computational power with the responsibility of sustainability is now a critical challenge facing the industry.
The Challenges of Computer Room Monitoring
It often takes a server room disaster to spur data management changes within an organization. While it’s always preferable for businesses to implement protective measures before a crisis occurs, excessive optimism and the routine of daily operations can make it easy to overlook the very real risks involved.
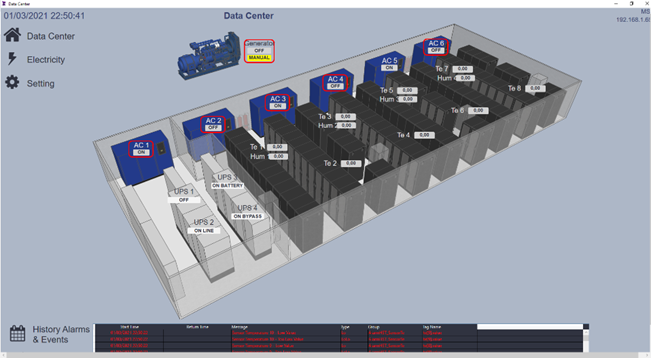
Key variables to monitor in a data center include temperature, humidity, power supply, server health, and security. Using a low-code template tailored for data center monitoring allows for real-time configuration of these variables, such as adjusting the number of servers, monitoring temperature fluctuations, and more. In this article, we will explore these aspects in greater detail.
Temperature and humidity
Temperature and humidity are critical factors in maintaining the health and performance of data center equipment. Excessive heat can cause servers and other hardware to overheat, potentially leading to malfunctions, reduced lifespan, or even catastrophic failures. Similarly, high humidity levels can result in condensation, which can damage sensitive electronic components, while low humidity can lead to static electricity buildup, posing a risk of electrical discharge. Proper environmental monitoring and control are essential to prevent these issues. Using real-time temperature and humidity sensors, data centers can ensure optimal conditions are maintained, reducing the risk of equipment failure and improving overall reliability.
For instance, adjusting the cold aisle temperature setpoint can lead to load fluctuations in the cooling infrastructure—such as chillers, cooling towers, heat exchangers, and pumps—resulting in nonlinear shifts in equipment efficiency. Ambient weather conditions and equipment control systems further influence the overall data center efficiency.
Power Supply
The power supply is a critical component in maintaining the continuous operation of a data center. Reliable and stable power is essential to ensure that servers, networking equipment, and cooling systems function without interruption. Any fluctuation or failure in the power supply can lead to costly downtime, data loss, or even damage to sensitive equipment. To mitigate these risks, data centers often rely on redundant power sources, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and backup generators to maintain a steady flow of electricity. Monitoring power usage in real-time with systems like HMI/SCADA enables operators to detect irregularities early and make necessary adjustments, optimizing power efficiency and reducing the chances of outages.
For example, power surges frequently occur due to lightning strikes, grid fluctuations, or faulty electrical components. Data centers commonly implement surge protection devices to prevent these incidents and utilize continuous power monitoring through HMI/SCADA systems. This enables early detection and automatic response to power abnormalities, helping to minimize disruptions and maintain smooth operations.
Server Health
Server health monitoring is vital for efficient data center management, as performance issues can lead to downtime, degraded functionality, or even data loss. By continuously tracking key metrics like CPU usage, memory load, disk performance, and network traffic, administrators can identify and address potential problems before they escalate. Real-time monitoring through an HMI/SCADA system provides a comprehensive view of server health, ensuring efficient resource allocation and maintaining peak performance of critical systems. A rule-based HMI/SCADA system further enhances this by enabling early detection of server overloads and failures, allowing for proactive interventions before serious issues occur.
For example, a data center could track CPU usage across multiple servers using server health monitoring. Suppose one server consistently runs near 100% CPU capacity due to increased user demand or a malfunctioning application. In that case, the monitoring system can be configured to trigger alerts when usage surpasses a predefined threshold, such as 85%. Upon detection, the HMI/SCADA system alerts administrators or automatically redistributes the workload across other servers, ensuring balanced performance and preventing potential system overloads or failures.
Security
Security is a fundamental aspect of technology, especially in data center management, where protecting sensitive equipment and valuable data from unauthorized access is a top priority. Data centers rely on surveillance systems, such as cameras and motion sensors, to provide constant monitoring, enabling rapid detection and response to potential breaches. By integrating these security systems with an HMI/SCADA platform, operators can manage and control security protocols in real time, significantly improving their ability to prevent unauthorized access and quickly address emerging threats.
A well-known example of a security breach related to data center infrastructure occurred in 2014 with the major US retailer Target. While the breach did not start directly within the data center, hackers used compromised credentials from a third-party HVAC vendor to gain unauthorized access to Target’s network. Once inside, they moved across the company’s systems and stole the financial and personal data of up to 110 million customers, eventually transferring this sensitive information to a server in Eastern Europe. The lack of network segmentation was a significant vulnerability, allowing attackers to move laterally through interconnected systems. This breach highlights the need to secure not only the data center but the entire ecosystem, emphasizing that security is the responsibility of everyone within an organization.
Low-code Template for Data Center Monitoring
ADISRA SmartView enables users to develop industry-specific low-code templates with minimal coding effort. It allows easy configuration of alarms, trends, recipes, reports, drivers, graphics, and more, all within the run-time environment.
Key ADISRA Low-Code Template Features for Enhancing Data Center Monitoring
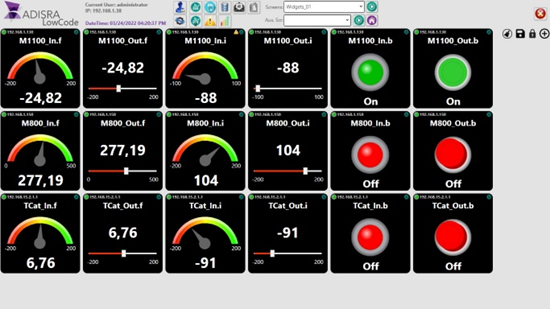
Real-time monitoring and visualization
Real-time monitoring and visualization enable continuous tracking, display, and analysis of data from various systems, processes, or environments as it is generated. Critical data center parameters, such as temperature, humidity, power consumption, and network traffic, are seamlessly integrated into dashboards through pre-built widgets, eliminating the need for complex coding. This approach allows users to instantly observe and respond to changes or potential issues, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Alarming and Notifications
The Low-Code Template features an intuitive alarm interface for defining alarms, categorizing them, and setting alarm states like high or low. Users can configure custom thresholds for key metrics such as temperature, power consumption, or server load. When these thresholds are exceeded, the system automatically triggers alerts, prompting operators to take immediate action. Alarms can be monitored within the application or forwarded to remote operators for a swift response.
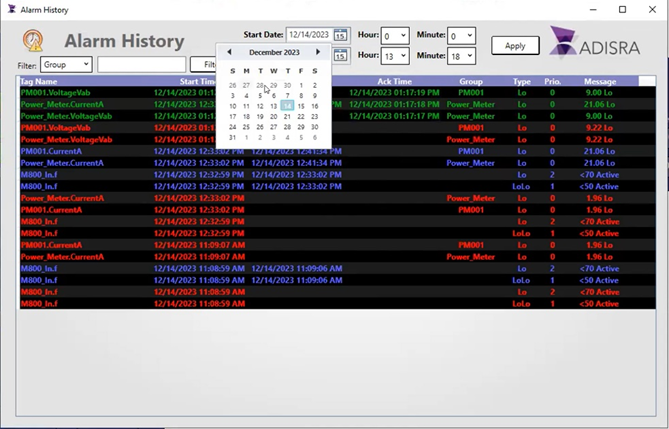
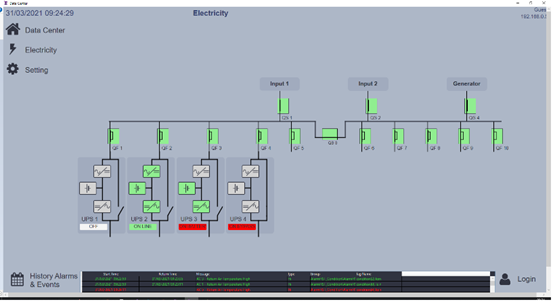
Connectivity
Connectivity in a data center is vital for the seamless integration of both physical sensors and enterprise systems. Sensors are strategically deployed throughout the facility to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, and power usage, ensuring continuous real-time data capture. ADISRA SmartView’s Low-code Templates enable users to connect to various sensors using the most common protocols for data centers, including Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), Modbus, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS), OPC UA, and MQTT.
Furthermore, SNMP support facilitates the integration of third-party management systems by sharing event information through SNMP traps, allowing the extension of monitoring capabilities. This feature enables the Enterprise Manager to monitor additional devices and sensors at a granular level.
HMI/SCADA systems such as ADISRA SmartView Low-code Template play a key role in managing this connectivity by serving as the central platform for visualizing and controlling data flows between sensors and enterprise systems. These platforms provide real-time interfaces where users can monitor data center operations, trigger alarms, and automate processes, ensuring efficient communication and coordination.
Power and energy management
Power and energy management is critical to maintaining a reliable computer room environment. HMI/SCADA systems such as the ADISRA SmartView Low-code template offer real-time visibility into power consumption, helping IT teams track energy usage trends and identify inefficiencies. These systems monitor the health and performance of backup power sources, such as Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems, providing detailed information on battery status and ensuring they are ready to support the load during a power outage. ADISRA Low-code Template with ADISRA SmartView expert system built-in can create predictive maintenance applications that detect early warning signs of potential power failures, such as voltage drops or surges, allowing for timely corrective action to prevent disruptions to critical operations. HMI/SCADA solutions enhance system reliability and contribute to significant cost savings over time by optimizing energy usage and proactively managing power systems.
Remote Access and Control
ADISRA SmartView Low-code Template allows IT staff to access and manage systems remotely, offering flexibility and efficiency in maintaining critical infrastructure. This capability allows for real-time monitoring and control of essential functions, such as adjusting air conditioning settings, managing backup power systems, and troubleshooting potential issues from anywhere with an internet connection. By enabling remote intervention, ADISRA SmartView minimizes downtime and reduces the need for on-site personnel, ensuring that problems are resolved swiftly and without the physical presence of IT staff in the computer room.
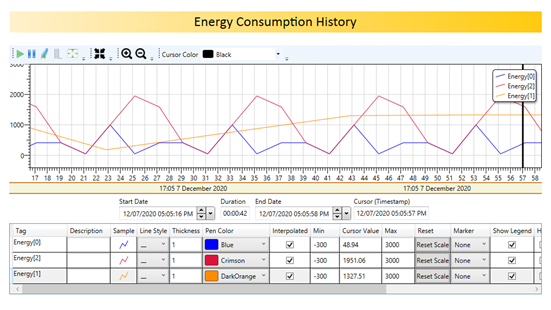
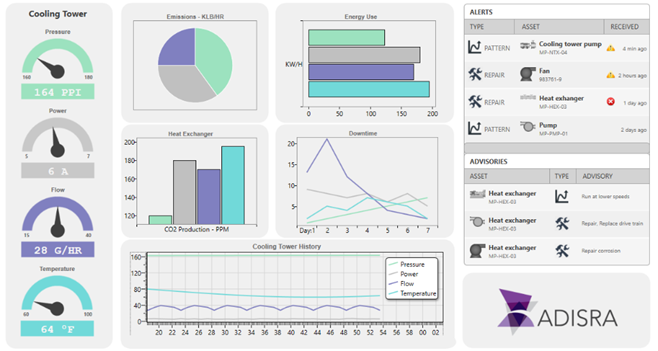
Historical Data and Reporting
Plotting historical data is crucial for uncovering patterns that may identify patterns and trends, making it possible to predict future issues. By leveraging this information, operators can implement proactive maintenance strategies, addressing problems before they escalate and avoiding costly downtime. The flexibility to create, delete, modify, or save trends during run-time is a key feature of the ADISRA Low-code Template for data centers. At run-time, users can visualize data points from multiple sources in a clear, graphical format, making it easier to interpret complex information. Additionally, users can configure history groups to store trend curves in real time, which can be saved in either a proprietary database or a standard SQL database for future analysis. This capability enhances both process monitoring and long-term performance optimization.
Conclusion
In an era where data centers are rapidly evolving to support the demands of AI and high-performance computing, efficient monitoring and energy management have never been more critical. Nvidia’s impressive growth, driven by AI workloads, places additional pressure on data centers to handle immense computational power, and sustainably. HMI/SCADA Low-code Templates, such as ADISRA SmartView Low-Code Template, offer an easy-to-use, comprehensive solution, providing real-time monitoring, automation, and energy management, crucial to maintaining operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. Integrating advanced monitoring technologies will ensure data centers will meet growing demands while staying energy-efficient and sustainable as the industry evolves.
