After spending more years than I would like to count working with Human Machine Interface (HMI) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) software, I began reflecting on how advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), cloud computing, the convergence of IT and OT, and the shift from desktops to mobile devices have reshaped the role of HMI/SCADA systems.
HMI/SCADA software was once focused primarily on local control and monitoring. It has evolved to seamlessly integrate with IIoT and edge computing, driving a more connected, data-driven, and intelligent approach to industrial automation. This transformation has enabled real-time insights, improved efficiency, and greater operational flexibility, redefining how industries monitor, analyze, and optimize their processes.
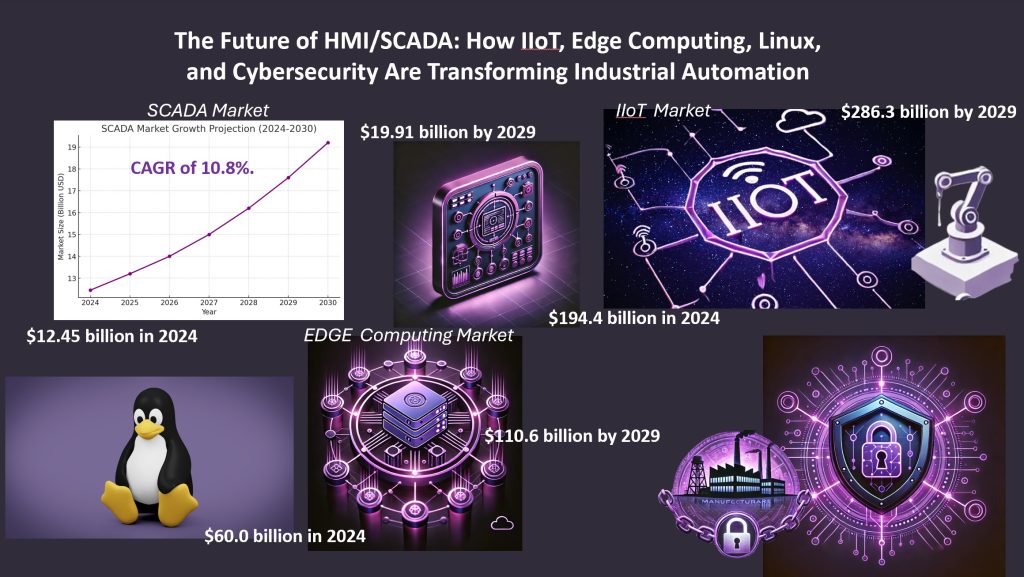
With the rapid advancement of technology and evolving industrial requirements, HMI/SCADA software is expanding its reach, unlocking new market opportunities. The SCADA market which stood at $12.45 billion in 2024, including hardware, software, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and HMI, is expected to experience significant growth. According to a January 2025 report by The Business Research Company, the market is projected to reach $19.91 billion by 2029, driven by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8%.
The rise of smart factories, powered by IIoT, edge computing, Linux-based systems, and enhanced cybersecurity, reshapes industrial operations by enabling real-time monitoring, intelligent decision-making, and optimized processes. These advancements are particularly significant for HMI/SCADA software, which now plays a central role in data integration, visualization, and control across complex industrial environments. To better understand their impact, let us explore how these key trends influence the evolution of HMI/SCADA systems.
The Continued Growth of IIoT
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has evolved significantly since its early adoption around 2010, built on decades of advancements in connected industrial devices, automation, and communication protocols. Over time, innovations in connectivity, data processing, and machine learning have solidified IIoT as a distinct and rapidly growing market segment.
IIoT adoption has accelerated in recent years, driven by increasing industry demand, evolving market dynamics, and breakthroughs in Artificial Intelligence (AI). As organizations continue to implement IIoT solutions, it remains a cornerstone of operational efficiency, productivity, and intelligent decision-making.
This expansion is expected to continue. According to Markets and Markets, the global IIoT market, valued at $194.4 billion in 2024, is projected to grow to $286.3 billion by 2029, with a CAGR of 8.1%.
IIoT and HMI/SCADA Software in 2025
By 2025, IIoT and HMI/SCADA software are expected to be more deeply embedded across industries, thanks to faster internet speeds, cost-effective sensors, and edge devices, and the rising demand for real-time, data-driven decision-making.
At the core of IIoT is data collection—the foundation of digital transformation and actionable insights. To enable seamless communication between industrial devices and systems, several key IIoT protocols have emerged, including Modbus, OPC UA, MQTT, and REST API, ensuring efficient data exchange between various layers of industrial operations.
ADISRA SmartView: Bridging the Gap Between IIoT and Industrial Automation
ADISRA SmartView is an HMI/SCADA software that integrates seamlessly with a wide range of industrial and IIoT protocols, enabling real-time data collection, visualization, and control. By bridging the gap between legacy systems and modern IIoT architectures, ADISRA SmartView helps organizations maximize IIoT benefits, enhance connectivity, and create a genuinely interconnected industrial ecosystem.
Experience ADISRA SmartView today—download a free trial from our website here.

The Rise of Edge Computing in Industrial Automation
As data generation becomes increasingly decentralized, most data is now created outside traditional data centers and cloud environments. According to Markets and Markets, the edge computing market is projected to grow from $60.0 billion in 2024 to $110.6 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 13%. This rapid expansion is not just a reflection of technological advancements but a shift toward a more distributed data model, revolutionizing real-time analytics by processing data closer to its source.
The Role of Edge Computing in HMI/SCADA
In HMI/SCADA software, edge computing enables real-time data collection from sensors and devices, local data processing, and faster decision-making based on analyzed information. This capability is essential for maintaining the efficiency, reliability, and responsiveness of industrial operations.
Key Benefits of Edge Computing
– Reduced Latency: Processing data on-site significantly decreases response time, which is crucial for real-time applications such as industrial automation, autonomous systems, and predictive maintenance.
– Improved Bandwidth Efficiency: Local data processing minimizes the amount of data transmitted to the cloud, reducing bandwidth consumption and network load.
– Enhanced Security: Sensitive data can be analyzed and anonymized at the edge before being transmitted, mitigating cybersecurity risks associated with centralized storage.
– Offline Functionality: Edge computing allows continuous data analysis and decision-making even in remote locations with limited or no internet connectivity.
– Analytics on the Edge: Real-Time Insights Where Data is Generated
edge analytics enables industries to monitor, analyze, and act on data in real-time without waiting for cloud-based processing. This ensures immediate responses to critical events, improving operational efficiency and system reliability.
ADISRA SmartView: Enhancing Edge Decision-Making
ADISRA SmartView, equipped with an integrated rule-based expert system, takes edge computing to the next level by applying predefined rules to real-time data. These rules, built on industry expertise, best practices, and regulatory standards, enable intelligent automation by:
– Automatically triggering alarms in response to critical conditions.
– Initiating corrective actions to prevent failures and optimize performance.
– Predicting potential failures before they occur, improving reliability, and reducing downtime.
By combining HMI/SCADA functionality with edge computing, ADISRA SmartView enables industries to collect, visualize, and analyze data closer to the source, leading to smarter, faster, and more efficient decision-making.
Learn More & Try ADISRA SmartView Today.
Read more about analytics at the edge in our previous blog here.
The Growth of Linux in Industrial Automation
Quantifying the market size and trends for Linux in industrial automation is challenging due to the diverse range of industries, applications, and devices involved. As an open-source operating system, Linux lacks a centralized tracking authority, making precise adoption data difficult to determine. However, Business Research Insight estimates that the global embedded Linux market, valued at $0.42 billion in 2023, is expected to grow to $0.74 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 6.57%.
Embedded Linux refers to the use of the Linux operating system in embedded systems rather than general-purpose computers. Its steady market growth is fueled by increasing demand for smart factories, IIoT applications, and connected systems. The rise of IIoT and edge computing has significantly expanded the use of embedded Linux in devices such as industrial sensors, industrial computers, robotics, automotive systems, and other connected technologies.
Key Factors Driving Linux Growth in Industrial Automation
1. Open-Source and Cost-Effectiveness
Linux’s open-source nature is a major factor in its widespread adoption. As a free and customizable platform, Linux eliminates licensing fees and enables users to modify and distribute the software to meet their specific industrial needs.
Additionally, the open-source development model fosters a strong community of contributors who continuously improve Linux, ensuring regular updates, bug fixes, and enhanced security features. This long-term support and stability make Linux a reliable choice for industrial automation, where uptime and security are paramount.
2. Security and Reliability
Security is a top priority in industrial automation, where systems manage critical processes, sensitive data, and safety operations. Linux offers robust security features and benefits from a vast developer community that actively monitors and improves its security measures. Its architecture allows for fine-tuned access controls, process isolation, and strong encryption protocols, making it a trusted platform for mission-critical applications.
3. Flexibility and Customization
One of Linux’s greatest advantages in industrial automation is its flexibility. Unlike proprietary operating systems, Linux allows for extensive customization, enabling developers to tailor the OS to specific industrial applications. Whether deployed on edge devices, embedded controllers, or cloud-based solutions, Linux can be optimized for performance, resource efficiency, and system compatibility.
4. Growing User Community and Open-Platform Adoption
Linux has a strong and active global community, providing resources, support, and shared knowledge for industrial developers. This collaboration accelerates innovation and problem-solving, making Linux an increasingly attractive choice for automation solutions.
A rising trend in industrial automation is the shift toward open platforms, where hardware and software components can be easily integrated and customized. Linux’s modular architecture and open-source compatibility align perfectly with this trend, allowing businesses to adapt and scale their automation systems with greater flexibility.
The Role of Linux in IIoT and Edge Computing
The growth of edge computing and IIoT is driving demand for secure, scalable, and adaptable operating systems that can manage data and applications at the edge of the network. With Linux’s lightweight footprint, security features, and real-time processing capabilities, it is an ideal choice for data acquisition, real-time analytics, and process control in industrial environments.
As industries digitize their operations, Linux-based systems are becoming increasingly critical in enabling automation, efficiency, and advanced analytics across manufacturing, energy, transportation, and other sectors.
ADISRA SmartView for Linux: Unlocking the Future of Industrial Automation
ADISRA SmartView for Linux allows users to design HMI/SCADA applications in a familiar Windows development environment while seamlessly deploying them to Linux-based systems. This hybrid approach bridges the strengths of both platforms, enabling businesses to:
– Leverage Windows development tools while benefiting from Linux’s stability and security.
– Utilize a built-in Remote Management Tool for enhanced operational oversight.
– Integrate seamlessly with leading Linux distributions for flexibility across deployments.
– Support industry-standard protocols, ensuring compatibility with IIoT and edge computing environments.
– Optimize deployment options for embedded and edge applications, meeting the demands of modern industrial automation.
ADISRA SmartView for Linux is more than just software—it’s a gateway to enhanced flexibility, efficiency, and control in industrial automation.
Learn more about Linux and ADISRA SmartView for Linux in our latest blog.
Experience ADISRA SmartView today—download a free trial here.
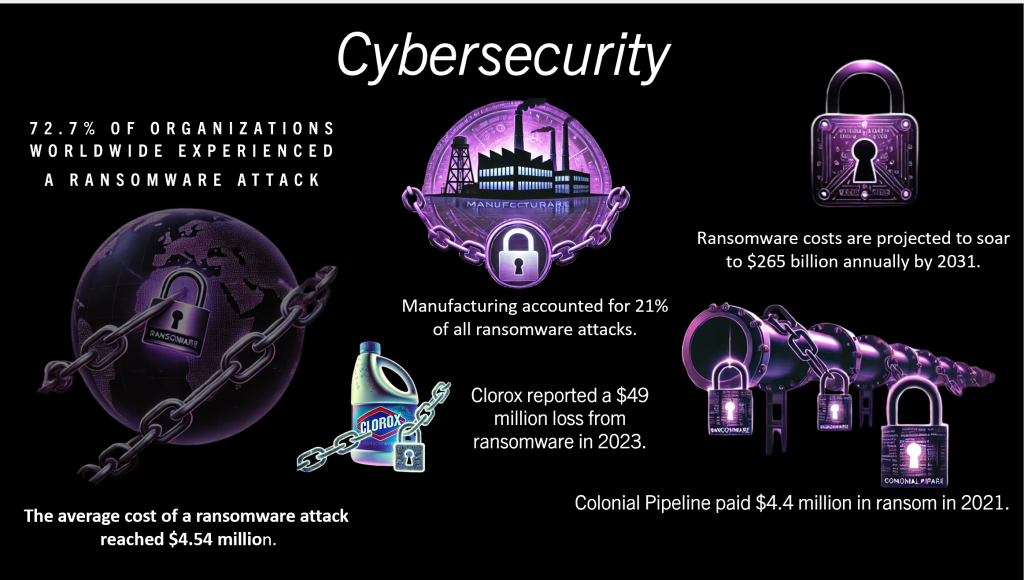
Increased Cybersecurity Focus in IIoT and Edge Devices
As IIoT and edge devices become more interconnected, they face unique cybersecurity challenges due to their critical role in industrial processes and often-limited security measures. These devices are prime targets for cyberattacks that can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and even pose physical safety risks. As connectivity expands, there is a growing emphasis on integrating robust cybersecurity features in industrial devices to safeguard critical data and infrastructure.
– To learn more about common security threats facing IIoT and edge devices, read our cybersecurity blog here.
Linux: A Secure Foundation for IIoT and Edge Computing
Linux plays a vital role in enhancing the security of Industrial IoT (IIoT) and edge computing environments. Its open-source nature, built-in security features, and active developer community make it a trusted platform for secure and reliable IIoT deployments.
Key Linux Security Features for IIoT and Edge Devices
– Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Linux enforces strict access control mechanisms, limiting what processes can access and modify system resources, reducing the risk of malware gaining control over devices.
– Kernel Hardening: Over time, the Linux kernel has been fortified with security features like stack protection, address space layout randomization (ASLR), and enhanced memory protections, helping mitigate vulnerabilities.
– Rapid Security Updates: The open-source community ensures continuous monitoring, allowing for fast security patches and updates to address newly discovered threats promptly.
– Secure Boot: Linux supports secure boot mechanisms, ensuring the integrity of the boot process and preventing unauthorized or malicious software from loading at startup.
– Encrypted Communication: Linux supports secure communication protocols such as TLS/SSL and SSH, protecting data transmitted between IIoT devices, edge computing nodes, and central servers from cyber threats.
For best cybersecurity practices, refer to our previous blog.
ADISRA SmartView: Built-in Security for Industrial Automation
Security is a top priority at ADISRA. ADISRA SmartView includes robust security features to protect industrial systems from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Key Security Features in ADISRA SmartView:
– LDAP Integration: Streamline authentication and access control with centralized user management.
– E-Signatures: Ensure compliance with industry standards by verifying critical actions.
– Traceability & Audit Logging: Track changes and user activities to enhance system accountability.
– User & Profile Management: Assign permissions based on user roles for controlled access.
– Profile-Based Permissions: Limit access to specific functionalities to protect sensitive operations.
Download our whitepapers below for more details on ADISRA SmartView’s security options.
Cybersecurity Beyond Software: A Holistic Approach
While built-in security features in HMI/SCADA software are essential, securing a single software package is not enough. Proper cybersecurity requires a comprehensive approach—securing the entire corporate security ecosystem, from network infrastructure to endpoint devices. Ensuring the security of the technology that underpins industrial operations is essential to protecting critical infrastructure.
Read our previous blog here for more cybersecurity best practices.
Download a free trial of ADISRA SmartView from our website here.
Conclusion
The industrial automation landscape is undergoing a significant transformation driven by IIoT, edge computing, Linux, and enhanced cybersecurity. HMI/SCADA software, once limited to local control and monitoring, now plays a critical role in real-time data collection, visualization, and intelligent decision-making across industrial environments.
As IIoT adoption accelerates, industries embrace faster data processing, cloud integration, and edge computing to enhance efficiency, security, and flexibility. The increasing reliance on Linux-based systems further strengthens scalability, reliability, and cybersecurity, making it a key enabler of the next generation of industrial automation.
Cybersecurity threats continue to evolve at the same time making robust security measures an essential part of any industrial digitalization strategy. ADISRA SmartView combines advanced HMI/SCADA capabilities, IIoT connectivity, edge intelligence, and built-in security features to empower organizations to operate smarter, safer, and more efficiently.
As industries continue their digital transformation, companies must adopt scalable, future-proof solutions to harness the full potential of IIoT, edge computing, and AI-driven automation. The shift toward connected, intelligent, and cyber-secure industrial operations is not just the future—it is happening now.
Learn more about IIoT, cybersecurity, and automation best practices in our previous blogs: cybersecurity. Edge computing, and Linux.
Experience the power of ADISRA SmartView—download a free trial today.
The Linux Foundation and The Linux Foundation logo design are registered
trademarks of The Linux Foundation. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus
Torvalds.
Tux, the Linux kernel penguin mascot, was created by Larry Ewing in 1996
[lewing@isc.tamu.edu] using the GIMP [www.gimp.org] and is not owned by The
Linux Foundation.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows 10X, Windows 11, and Windows Designs are trademarks
of the Microsoft group of companies.
ADISRA®, ADISRA’s logo, InsightView® and KnowledgeView® are registered trademarks of
ADISRA, LLC.
Copyright
© 2025 ADISRA, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
